Cancer
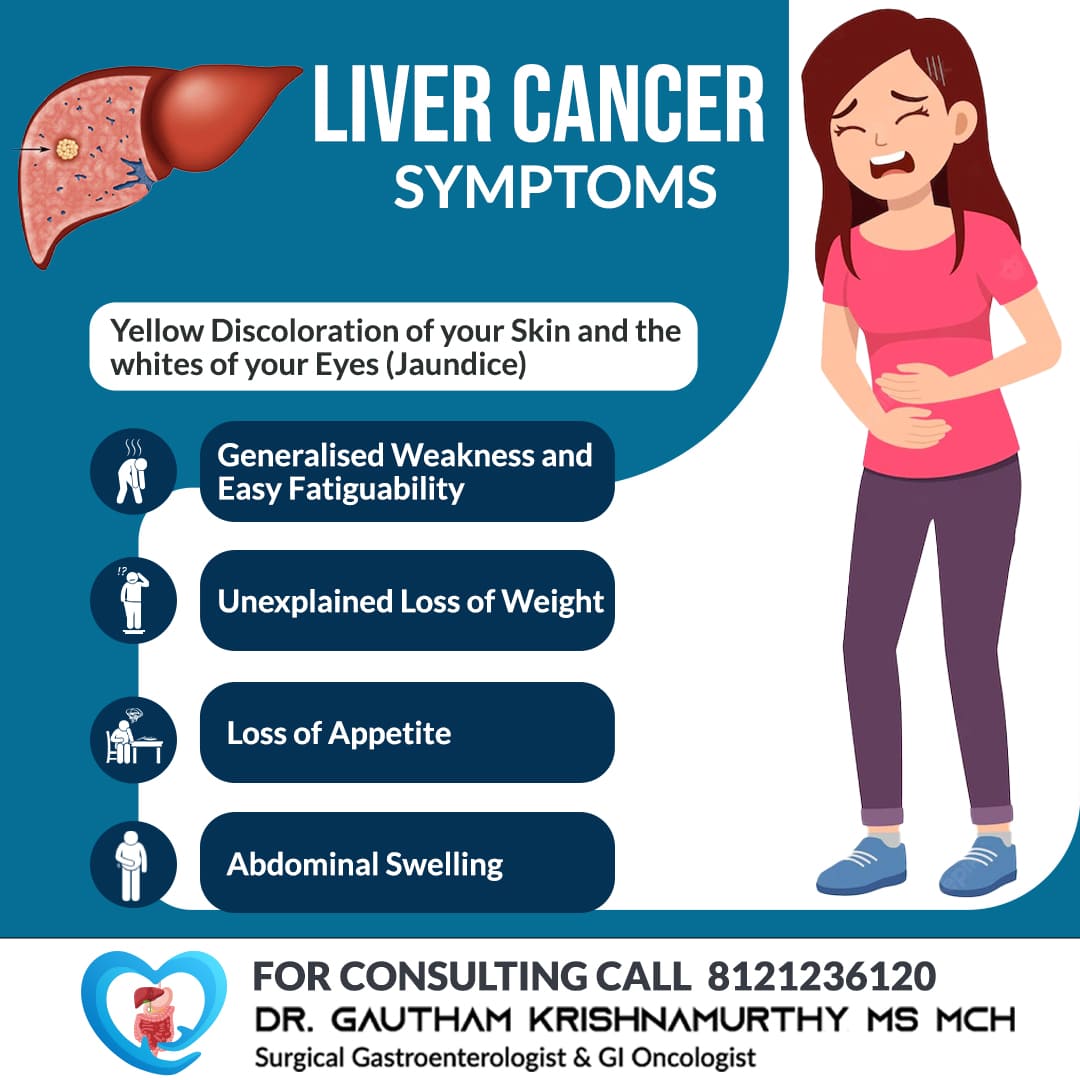
Cancer refers to the abnormal growth of abnormal cells. Effective treatment is available for all cancers. Cancers are potentially curable at early stages.
Request An AppointmentLaparoscopy
Surgical technique to perform abdominal surgeries through small incisions. Complex surgeries such as cancer surgeries can also be effectively treated using laparoscopy.
Request An AppointmentPancreas
Pancreas is an abdominal organ affected by inflammatory conditions and cancer. Conditions affecting pancreas can cause abdominal pain, jaundice, diabetes mellitus and malabsorption.
Request An AppointmentIrritable bowel syndrome
IBS is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by long standing abdominal pain which may or may not be associated with bowel disturbances such as diarrhea and constipation.
Request An Appointment